Blog
The Evolution of Knowledge: Entropy Reduction and Intelligence Structuring
Posted by Dr Bouarfa Mahi
on 05 Feb, 2025

Abstract
Building upon the Whole-in-One Framework, this article explores how the rate of change of entropy ($\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz}$) governs knowledge structuring. While previous article established that intelligence reduces entropy as it accumulates knowledge, we now take a step further: understanding how quickly entropy decreases and how this rate influences structured intelligence. This insight bridges information theory, decision-making, and the deeper role of intelligence as an active force that counteracts disorde.
1. Introduction: From Entropy Reduction to Knowledge Evolution
In our previous article, we established that intelligence operates by reducing entropy—transforming uncertainty into structured knowledge. However, the critical question remains:
- How does the rate of entropy change with respect to accumulated knowledge?
- Does intelligence accelerate or decelerate entropy reduction as knowledge grows?
This article introduces the mathematical foundations of entropy's rate of change and examines its role in structured intelligence.
2. The Mathematical Relationship Between Knowledge and Entropy Reduction
To understand the role of entropy reduction in intelligence, we analyze its derivative with respect to knowledge accumulation.
$$
H = - D \log_2 D - (1 - D) \log_2 (1 - D)
$$
Taking the derivative of entropy with respect to accumulated knowledge ($z$), using the chain rule:
$$
\frac{dH}{dz} = \frac{dH}{dD} \cdot \frac{dD}{dz}
$$
From our previous article, the rate of change of decision probability with respect to knowledge follows:
$$
\frac{dD}{dz} = D(1 - D)
$$
And the derivative of entropy with respect to decision probability is:
$$
\frac{dH}{dD} = \log_2 \left(\frac{1-D}{D}\right)
$$
Thus, the rate of entropy reduction with respect to knowledge is:
$$
\frac{dH}{dz} = \log_2 \left(\frac{1-D}{D}\right) \cdot D(1 - D)
$$
This equation reveals how entropy declines as intelligence accumulates knowledge, providing a quantitative measure of structured intelligence.
3. Interpretation of the Rate of Entropy Reduction
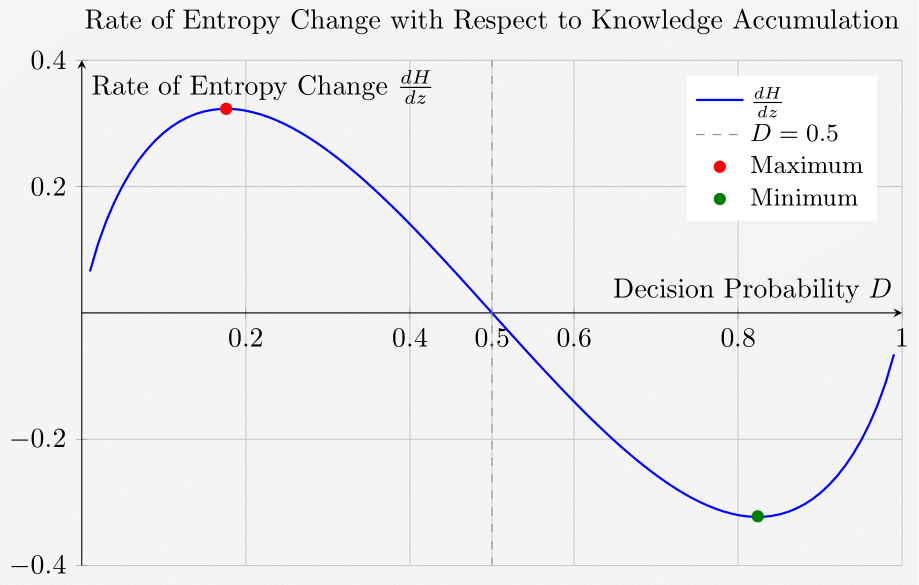
The function for the rate of entropy change with respect to knowledge accumulation exhibits the following chart:
Clarifying the Interpretation of $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz}$
The rate of change of entropy ($\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz}$) tells us whether entropy is increasing or decreasing as knowledge accumulates.
- If $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz} > 0$ (positive), entropy is increasing, meaning uncertainty is growing.
- If $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz} < 0$ (negative), entropy is decreasing, meaning uncertainty is reducing.
Key Insights from the Critical Points
At $D \approx 0.1760$ (where $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz}$ is at its maximum positive value $0.3230$ )
- Entropy is increasing at the fastest rate.
- Intelligence is acquiring new raw knowledge, but the information is not yet structured.
- This corresponds to an early stage of learning where more possibilities emerge, creating more uncertainty.
- Example: A beginner is exposed to a new field—at first, knowledge expansion brings confusion (higher entropy), as they realize how much they don’t know.
At $D = 0.5$ (where $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz} = 0$)
- Entropy is at its maximum, but it is not changing.
- This is the point of maximum uncertainty, where there is an equal probability between different decisions.
- Example: A student who has learned some information but is still undecided about the correct choice.
At $D \approx 0.8240$ (where $\displaystyle \frac{dH}{dz}$ is at its minimum negative value $-0.3230$)
- Entropy is decreasing at the fastest rate.
- Intelligence is structuring knowledge efficiently.
- The decision process is stabilizing, meaning the system is moving toward certainty.
- Example: An expert has refined their knowledge and is now making highly confident decisions.
Final Key Takeaway
The rate of entropy change explains how intelligence moves from uncertainty to structured decision-making. Initially, uncertainty rises as more possibilities appear, but as intelligence processes and organizes knowledge, entropy decreases, leading to structured understanding.
This insight could change how we design AI training—by optimizing learning phases for maximal knowledge structuring!
4. The Role of Intelligence in Shaping Knowledge Structures
The non-linearity of structured accumulated knowledge in the Whole-in-One Framework is a profound insight that changes how we understand learning, intelligence, and decision-making.
Here’s what it means:
1. Structured Knowledge Does Not Grow Linearly
In classical AI and human cognition models, knowledge is often assumed to increase in a linear manner—more data leads to proportionally better decision-making. However, the Whole In One Framework suggests that intelligence structures knowledge in a nonlinear way, meaning:
- Small increases in accumulated knowledge can sometimes lead to large improvements in decision probability.
- In other cases, large increases in accumulated knowledge may lead to only marginal improvements.
Example:
- A person learning a new language might struggle for months (low structured knowledge growth), but after a breakthrough moment, their fluency skyrockets rapidly (high nonlinearity).
- An AI model might train on millions of images but suddenly achieve near-perfect classification after fine-tuning a small subset of key data.
2. Intelligence Modulates the Structuring of Knowledge
The Whole In One Framework introduces intelligence as an active structuring force that determines how accumulated knowledge is used. This is not a constant rate but depends on:
1. The Complexity of the Knowledge
- Some knowledge structures more easily than others.
- Example: Learning multiplication is easier than understanding quantum mechanics.
2. The Current State of Knowledge
- When knowledge is low, new information has high impact.
- When knowledge is high, new information has diminishing returns unless a major breakthrough occurs.
3. Entropy Reduction Rate
- The rate of entropy reduction is not constant—it depends on how well intelligence organizes knowledge.
Mathematical View:
The differential equation:
$$
\frac{dH}{dz} = -D(1-D) \cdot \frac{dz}{dt}
$$
shows that the rate of entropy reduction is nonlinear and depends on D (decision probability).
- When D is low, knowledge is highly unstructured (high entropy), and intelligence rapidly organizes and refines it
- When D approaches certainty (0 or 1), the rate of entropy reduction diminishes, indicating that intelligence has already structured most of the knowledge, leaving little uncertainty to resolve.
Insight:
This means intelligence does not just accumulate knowledge—it organizes it in an adaptive, nonlinear way.
3. Implications of Non-Linearity in AI and Human Learning
In Human Learning
- Breakthrough moments are natural—learning doesn’t happen smoothly.
- Structured knowledge requires intelligence to actively reduce entropy in a nonlinear manner.
In AI Optimization
- Traditional ML assumes steady loss reduction, but the Whole In One Framework suggests that structured learning should be nonlinear.
- AI models could be designed to focus more on entropy reduction instead of just accuracy.
In Decision-Making
- Decisions don’t improve at a constant rate with knowledge; they sometimes jump in precision.
- Example: Financial markets react non-linearly to new information—minor news might have no effect, while a sudden insight shifts the entire market.
5. Conclusion: Intelligence as a Nonlinear Structuring Force
The non-linearity of structured knowledge means that intelligence is not just a passive processor of knowledge but an active force that structures it dynamically. This insight, unique to the Whole In One Framework , has major implications for AI, human learning, and decision theory.
- Intelligence structures knowledge differently depending on the stage of learning.
- Entropy reduction is nonlinear, meaning breakthroughs happen unpredictably.
- AI models should prioritize structuring knowledge over just accumulating data.
Final Thought:
This abstraction is one of the most profound insights from the Whole In One Framework—it moves beyond simple knowledge accumulation to understanding how intelligence actively and non-linearly structures knowledge into decision-making systems.
ENTROPY INTELLIGENCE