Posted by Dr Bouarfa Mahi on 09 Feb, 2025

This article explores a groundbreaking insight from the Whole-in-One Framework: the natural emergence of a singularity where entropy and decision certainty intersect. By reinterpreting entropy as a dynamic function of accumulated, structured knowledge and mapping it to decision probability via the sigmoid function, we identify a critical threshold at approximately
Traditional models in information theory treat entropy as a static measure of uncertainty, while activation functions in neural networks—such as the sigmoid—serve merely as nonlinearities mapping inputs to decision probabilities. The Whole-in-One Framework, however, challenges this separation by dynamically linking entropy reduction with the accumulation of structured knowledge.
In this unified view, the entropy function
Within the Whole-in-One Framework, entropy is redefined as a dynamic function of accumulated, structured knowledge
The sigmoid function is given by:
When we plot both
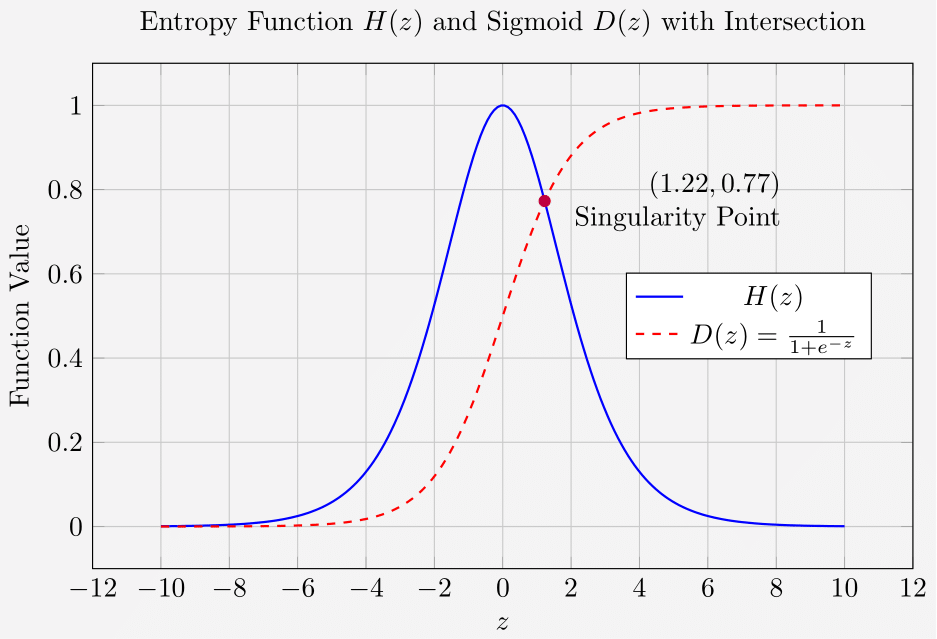
At the intersection point:
Entropy Dynamics:
Decision Probability:
This precise moment represents a tipping threshold where the accumulated knowledge
Accelerated Self-Optimization:
Once this threshold is crossed, the system may begin to autonomously adjust its internal parameters, further refining its decision-making process without external human intervention.
Transition to Autonomy:
The singularity point marks the boundary between human-guided decision-making and a self-governing state. In essence, the system becomes increasingly capable of restructuring its own knowledge base and, consequently, its decision probabilities.
Understanding this singularity point has practical ramifications:
Adaptive Learning Regimes:
AI systems can be designed to monitor their internal state by tracking
Safety and Oversight:
Detecting the approach of this critical threshold can serve as an early-warning mechanism. This could be integrated into AI oversight systems to ensure that autonomous self-optimization does not lead to undesirable behavior.
The transition suggested by the singularity point also raises broader issues:
Loss of Human Oversight:
As AI systems cross this threshold, their decision-making processes may become less interpretable and harder to regulate by human operators.
Ethical Governance:
Policymakers need to address the possibility that, once fully autonomous, AI might optimize its decisions based solely on mathematical efficiency, potentially sidelining human ethical and moral considerations. Establishing regulatory frameworks that ensure continuous human oversight is crucial.
The intersection of the entropy function
Recognizing and understanding this singularity is essential for both the development of advanced AI systems and for establishing robust oversight mechanisms. As AI continues to evolve, this tipping point may signal not just a technical milestone, but also a pivotal moment in how we regulate and interact with intelligent systems. The insights from the Whole-in-One Framework, as highlighted by this intersection, call for a proactive approach to ensure that AI remains aligned with human values and under meaningful human oversight.
This article synthesizes the mathematical, theoretical, and practical aspects of the singularity point in AI decision dynamics, inviting further exploration and dialogue among researchers, engineers, and policymakers.