Posted by Dr Bouarfa Mahi on 18 Feb, 2025

Understanding Entropy and Knowledge Accumulation in Neural Networks
In this article, we explore the concept of entropy in neural networks and its role in tracking the accumulation of knowledge during the forward pass. We introduce a simple neural network diagram and demonstrate how entropy can be calculated at each forward pass, reflecting the uncertainty in the model’s predictions. This approach emphasizes the importance of understanding the evolution of decision confidence over time. Furthermore, we present a practical implementation of the entropy tracking system using the z-domain mapping, offering insights into how entropy can guide the learning process in neural networks.
In the field of artificial intelligence (AI), the concept of entropy plays a crucial role in understanding the uncertainty and information contained in a model’s predictions. As AI systems evolve, they accumulate knowledge, which can be tracked through entropy. The reduction of entropy is often seen as an indicator of a model’s increasing decision confidence. However, this relationship is not always easy to visualize and quantify.
In this article, we present a simple neural network example with one hidden layer and one output neuron. We compute the entropy at each forward pass, which allows us to track how the model’s uncertainty decreases over time. The central idea is that the accumulation of knowledge in the model is reflected by a decreasing entropy value, corresponding to more structured decision-making. We also introduce a method for implementing entropy tracking using the z-domain, a unifying framework for knowledge accumulation.
Consider a simple neural network with the following components:
The forward pass in this network can be computed as:
Where:
This equation gives the output of the model,
Entropy,
Where:
The entropy value reflects how much uncertainty is present in the network's predictions. As the model learns and accumulates knowledge, entropy decreases, which indicates that the network is becoming more confident in its predictions. This process can be observed after each forward pass as the entropy value is updated.
The neural network shown in the diagram below calculates the entropy at each forward pass. The input layer consists of 5 neurons, and the output layer has a single neuron, denoted as
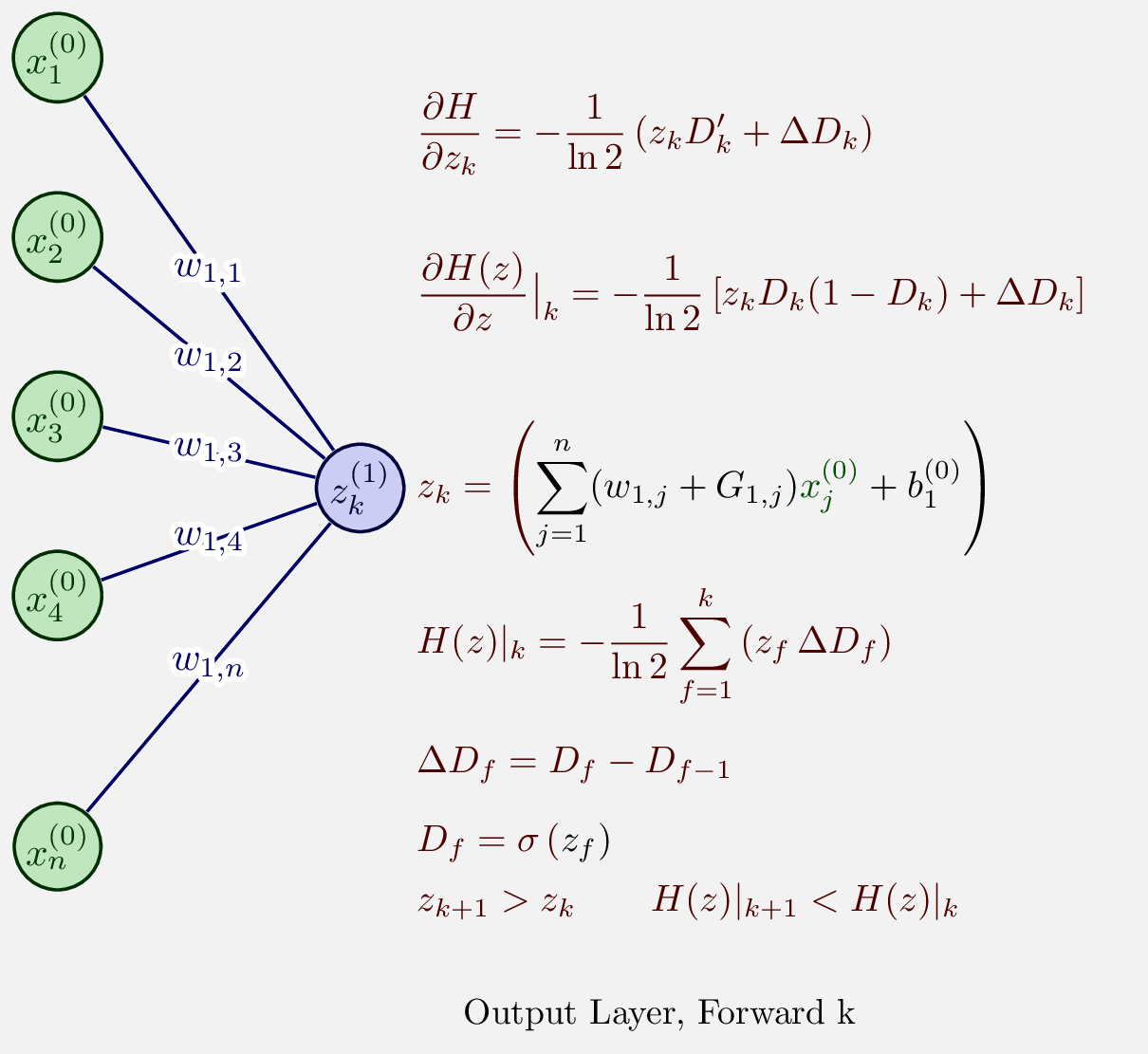
In this network, we track the entropy after each forward pass to see how the uncertainty in the model’s predictions decreases as it learns.
The z-domain serves as a unified framework for modeling the accumulation of knowledge in AI systems. By mapping raw input data into a cumulative representation, the z-domain tracks how knowledge evolves over time. Each step
Where:
In this framework, the z-domain provides a natural progression of knowledge accumulation. By monitoring how
To ensure that the knowledge accumulation process is smooth and controlled, we introduce a dynamic learning rate adjustment mechanism. This mechanism ensures that the updates to the network’s weights produce positive and bounded increases in knowledge. The learning rate,
This dynamic adjustment helps ensure that the network's learning process is gradual and consistent for the discrete case:
The update rules are:
where
This article introduces a method for tracking entropy in neural networks, offering insights into the process of knowledge accumulation. By calculating entropy at each forward pass and updating it dynamically, we can monitor how the network's predictions evolve and become more structured over time. The z-domain framework allows for a unified representation of knowledge accumulation, ensuring that the learning process is gradual and controlled.
Through the combination of entropy calculation and the z-domain framework, we can gain a deeper understanding of the model's decision-making process, providing a valuable tool for building adaptive, efficient, and interpretable AI systems. This approach offers a new way to think about the intersection of knowledge, uncertainty, and decision-making, which could have profound implications for future AI development.